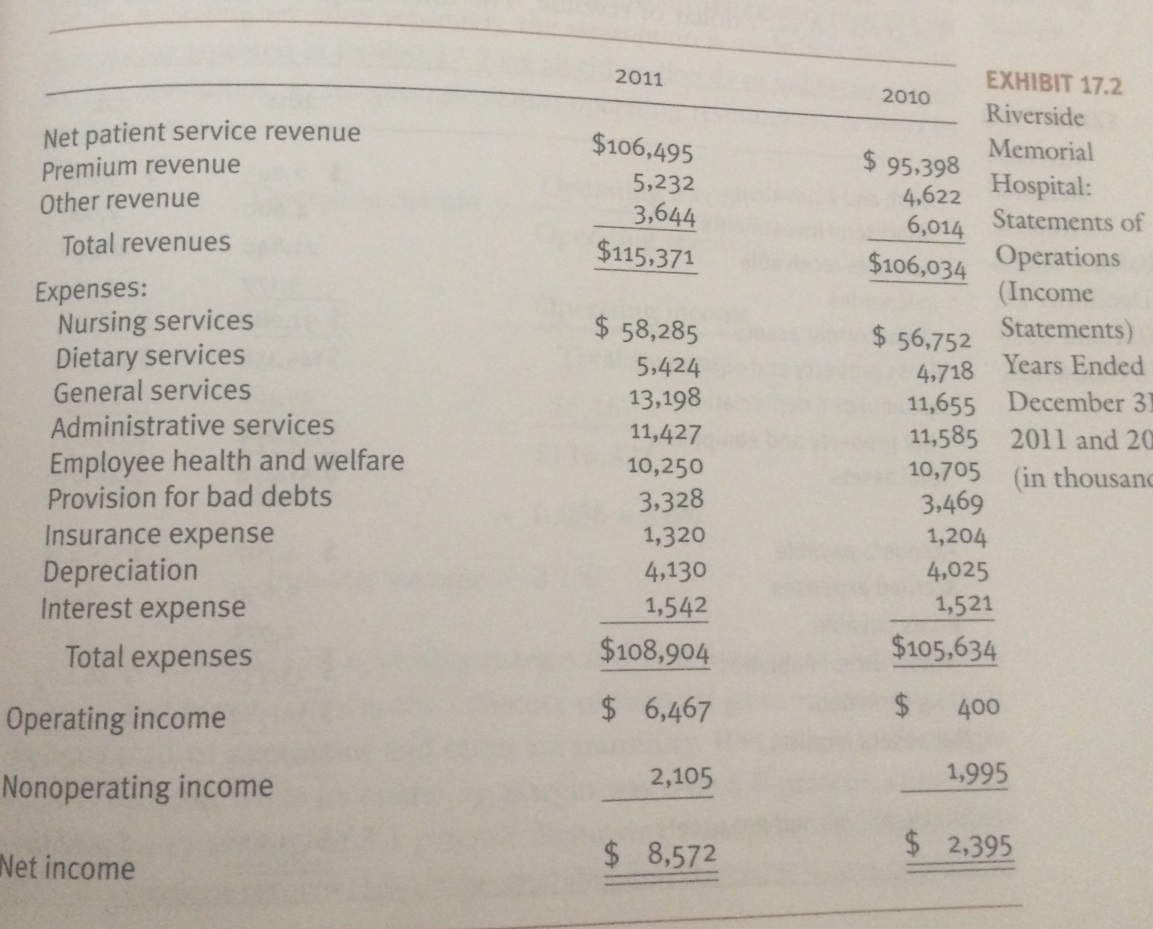
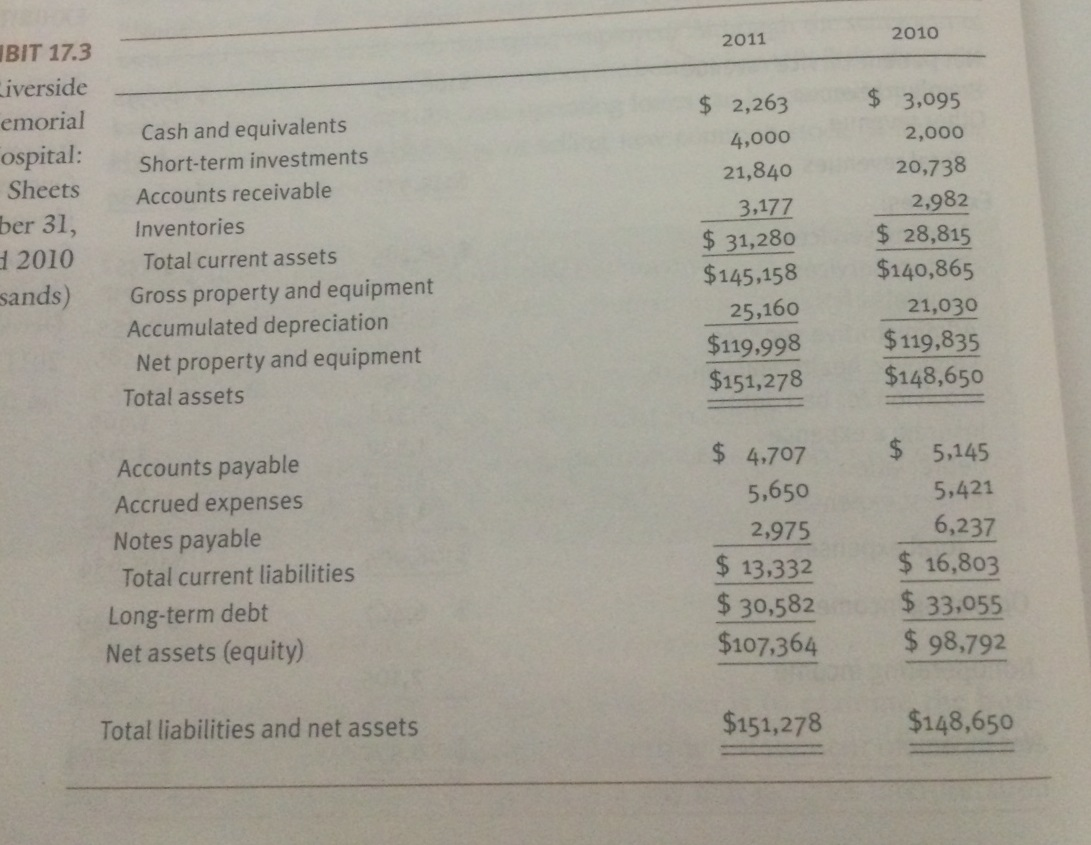
Riverside Memorial’s Primary Financial statements are prsented in exhibits 17.1, 17.2 and 17.3 (attached)
A. Calculate riversids financial ratios for 2010, assume that riverside had $1,000,000 in lease payments and 1,400,000 in debt principal repyments in 2010.
B. Interpret the ratios. Use both trend and comparative anaylyses. for the comparative analysis assume that the industry average data prsented in the book is valild for both 2010 and 2011.
from the Health care finance: an introduction to accounting and fianacial managment 5th edition by louis c. gapenski

(A). Riversids financial ratios for 2010, are as follow.
Working Capital = Current Assets – Current liabelity
The ratio is a popular financial ratio used to test a company’s lequidity (also referred to as its current or working capital position) by deriving the proportion of current assets available to cover current liabilities.
= 28815-16803
=12,012
Current ration = Current Assets / Current Liabelity
=28,815/ 16,803
=1.71
Quick ratio
The Quick ratio or the acid-test ratio – is a liquidity indicator that further refines the current ratio by measuring the amount of the most liquid current assets there are to cover current liabilities. The quick ratio is more conservative than the current ratio because it excludes inventory and other current assets, which are more difficult to turn into cash. Therefore, a higher ratio means a more liquid current position
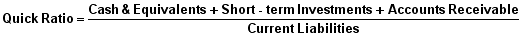
=25833/16803
=1.53
Profitability Indicator Ratios: Profit Margin Analysis
Positive profit margin analysis translates into positive investment quality. To a large degree, it is the quality, and growth, of a company’s earnings that drive its stock price.
Formulas:
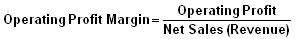
= 400/106034
=0.3%
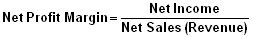
=2395 /106034
=2.25%
Profitability Indicator Ratios: Return On Assets
Formula:
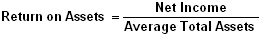
=2395 / 148650
Return On Capital Employed
=1.61%
This ratio indicates how profitable a company is relative to its total assets. The ROA ratio illustrates how well management is employing the company’s total assets to make a profit. The higher the return, the more efficient management is in utilizing its asset base. The ROA ratio is calculated by comparing net income to average total assets, and is expressed as a percentage.
Profitability Indicator Ratios: Return On Equity
This ratio indicates how profitable a company is by comparing its net income to its average shareholders’ equity. The return on equity ratio (ROE) measures how much the shareholders earned for their investment in the company. The higher the ratio percentage, the more efficient management is in utilizing its equity base and the better return is to investors.
Formula:
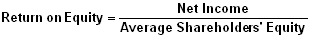
= 2395/ 98792
=2.42%
By comparing net income to the sum of a company’s debt and equity capital, investors can get a clear picture of how the use of leverage impacts a company’s profitability. Financial analysts consider the ROCE measurement to be a more comprehensive profitability indicator because it gauges management’s ability to generate earnings from a company’s total pool of capital.
Formula:
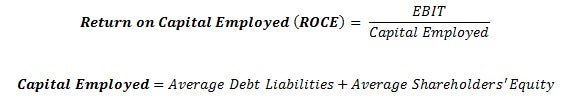
=2395 / 33055+98792
= 2395/141874
=1.81%
Debt Ratios: Debt-Equity Ratio
the debt-equity ratio provides another vantage point on a company’s leverage position, in this case, comparing total liabilities to shareholders’ equity, as opposed to total assets in the debt ratio. Similar to the debt ratio, a lower the percentage means that a company is using less leverage and has a stronger equity position.
Formula:
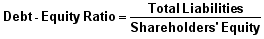
= 49858/98792
=0.5046
Cash Flow Indicator Ratios: Operating Cash Flow/Sales Ratio
Formula:
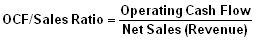
=11,196 / 106,034
=10.56%
Free Cash Flow/Operating Cash Flow Ratio
The cash flow remaining after this deduction is considered “free” cash flow, which becomes available to a company to use for expansion, acquisitions, and/or financial stability to weather difficult market conditions. The higher the percentage of free cash flow embedded in a company’s operating cash flow, the greater the financial strength of the company.
Formula:

=11,196-4296/ 11,196
=6900/11196
=61.62%
